A Guide to Popular Fast Food Packaging Materials and Their Pros and Cons
Plastics, paper, metals, and new composites are used for fast food packaging. Plastics are the most common. They make up about 62% of the market. Plastics protect food and are cheap to use. Looking at the good and bad sides of each type helps people choose better. Packaging changes the price, food safety, and the environment. It can also change how people see a brand.
Picking the best fast food packaging can change food freshness and how much customers like a brand.
|
Packaging Material |
Pros |
Cons |
|---|---|---|
|
Plastic |
Strong, leak-proof, keeps food fresh |
Pollution, health concerns, slow to degrade |
|
Paper |
Recyclable, lightweight, good branding |
Less heat retention, can cause deforestation |
|
Aluminum |
Durable, recyclable, heat-resistant |
High energy cost, not great for cold foods |
|
Biodegradable |
Eco-friendly, reduces waste |
More expensive, less durable |
Key Takeaways
-
Fast food packaging uses plastics, paper, metals, glass, and composites. Each material has its own good and bad points. Plastic is strong and cheap. But it can pollute and is hard to recycle. Paper and cardboard are light and can be recycled. But they do not keep food safe from water unless coated. Metal and glass keep food fresh and can be recycled. But they cost more and can be heavy or break easily. Eco-friendly packaging is becoming more popular. These include biodegradable and compostable materials. They help cut down on waste and protect the environment.
Fast Food Packaging Overview
Common Food Packaging Materials
Fast food places use many food packaging materials for different needs. The most common types are:
- Plastic and Bioplastics: These are strong and cheap. PET and PP are used a lot. Bioplastics like PLA can break down in compost.
- Paperboard and Coated Paper: Many restaurants use these for wraps, trays, and boxes. Some coatings make recycling harder.
- Molded Fiber: This comes from bagasse or bamboo pulp. It is compostable and stands up to heat. It is good for plates and bowls.
- Aluminum and Specialty Materials: Aluminum keeps food hot and can go in the oven. It is used for catering and some takeout foods.
- Glass: Some fancy fast food uses glass for tight seals. Glass is heavy and breaks easily, so it is not used much.
- Biodegradable and Compostable Materials: These include wraps made from plants or seaweed. They break down on their own and are good for the environment.
Food packaging materials come in many shapes. You see them as cups, boxes, plates, and wraps. Fast casual restaurants pick nicer materials. They want to look good and help the planet.
Importance in the Industry
Picking the right food packaging materials is very important in fast food. Good packaging keeps food safe and warm. It stops spills and messes. It also helps show off a brand with logos and colors. In the last ten years, more places use sustainable fast food packaging. Companies use compostable paper and plant-based wraps. Some even use packaging you can eat to cut down on trash.
Smart packaging uses QR codes and freshness labels. These help customers learn how to recycle and check food quality. Good packaging design lets workers pack food fast and keeps it safe while moving. Big chains like McDonald's and Wendy’s now use more recycled and renewable materials. This helps the earth and makes customers happy. The best food packaging materials save money, cut waste, and keep people coming back. Because of this, food containers and packaging are now a big deal for restaurants and customers.
Plastic Packaging

Plastic Types
Fast food places use different plastics for containers and wraps. Each plastic type has special features for certain uses. The table below lists the main plastics used in fast food packaging:
|
Plastic Type |
Common Use in Fast Food Packaging |
Distinguishing Properties and Additives |
|---|---|---|
|
Polyolefins (Polyethylene, Polypropylene) |
Films, containers, wraps |
These are strong and bend easily. They do not cost much. Additives help them slide, last longer, and stay strong in bad weather. |
|
Polystyrene (PS) |
Cups, trays, clamshells |
This plastic is clear and tough. It can handle heat because of special stabilizers. |
|
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) |
Some films, containers |
PVC is strong and bends well. It can take heat better with stabilizers. |
These plastics let companies make many shapes and sizes. Polyolefins are good for wraps and boxes. Polystyrene is used for cups and trays. PVC is found in some special packaging.
Pros and Cons
Plastic packaging is still used a lot in fast food for many reasons:
- Durability and Strength: Plastics keep food safe from water, air, and germs. This helps food last longer and cuts down on waste.
- Versatility: Plastics can be made into many shapes. This makes them good for lots of foods.
- Lightweight: Plastics are light, so shipping is cheaper and easier.
- Visibility: Clear plastic lets people see their food. This helps customers trust what they get.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Plastics usually cost less than glass or metal.
- Leak-Proof and Microwave-Safe: Many plastic containers stop spills and can go in the microwave.
Note: Plastic packaging keeps food fresh and is easy to use, but it also has problems.
But there are some big problems too:
- Plastics stay in the earth for a very long time. They cause pollution in land, water, and trash dumps.
- Only about 35% of packaging waste gets recycled or composted.
- Making and throwing away plastics puts bad gases and chemicals into the air.
- Some plastics can let chemicals get into food, especially when hot.
- Animals and nature can get hurt by plastic trash.
The good and bad sides of plastic packaging show why companies look for other choices like molded fiber or bioplastics. Still, plastics are used a lot in fast food because they have special benefits.
Paper and Cardboard Packaging

Paperboard Types
Fast food places use many kinds of paper and cardboard. Corrugated fibreboard is made from kraft paper. It has layers that help protect food from bumps. This is good for burgers, pizza, fries, and meal packs. Kraft paper is strong and lets air in. It breaks down in nature, so it is good for bread and dry foods. Greaseproof paper has a silicone layer. It stops oil and works for hot, greasy foods like fried chicken. Wax paper has a wax layer. It keeps sandwiches and burgers fresh by blocking water and air. Food-grade coated paper keeps out oil and water for many foods. White cardboard looks fancy and is used for cakes and desserts. It often needs a lining to stop grease. Virgin fiber cardboard is made from new wood pulp. It is strong and clean. Recycled cardboard uses old paper and helps the planet. Some cardboards have special layers to stop oil from leaking.
- Kraft paper: Strong, breaks down, helps the earth
- Greaseproof paper: Stops oil, handles heat
- Wax paper: Blocks water and oil
- Food-grade coated paper: Keeps out oil and water
- White cardboard: Looks nice, can be printed, needs lining for grease
- Virgin fiber and recycled cardboard: Strong, good for the planet
Pros and Cons
Paper packaging is getting more popular in fast food. It is better for the earth and can be recycled. Many food boxes now use paperboard to use less plastic. Most paper and cardboard can be recycled about seven times. This saves energy and helps stop cutting down trees. Some paper can be composted, but this is not as common as recycling.
Paper and cardboard packaging are good for the earth, but they have some problems.
|
Aspect |
Pros |
Cons |
|---|---|---|
|
Barrier Properties |
Breaks down, can be recycled, used again, good for the earth |
Does not stop water and air well, food does not last long unless coated |
|
Environmental Impact |
People like it, cuts down on plastic trash |
Brea ks down slowly in dumps, can make methane gas |
|
Practical Use |
Used for many foods, easy to change for different foods |
Needs special layers for oily or wet foods |
Paper packaging is best for foods eaten soon and for dry foods. It does not work well with water or for keeping food long unless it has a coating. It can be recycled and breaks down, but coatings and food bits can make recycling harder. Still, using more paper and cardboard shows fast food places want to help the earth.
Metal Packaging
Metal Types
Fast food places use different metals for packaging. Each metal has special features that help keep food safe and fresh. The table below lists the main metals used in fast food packaging and how they are used:
|
Metal Type |
Typical Forms in Fast Food Packaging |
Typical Applications and Properties |
|---|---|---|
|
Aluminium |
Foil, cans, laminated and metallized films, retort pouches, collapsible tubes, bottles, caps, closures |
Lightweight, does not rust, used for drinks, seafood, pet food, and baked goods; easy to recycle; used for both soft and hard packaging |
|
Tinplate (Coated Steel) |
Three-piece cans, rigid containers |
Steel with a tin layer for strength and to block leaks; good for drinks and foods that need to stay clean; needs a coating to stop food from touching metal; can be recycled and is magnetic |
|
Tin-Free Steel |
Like tinplate but no tin coating |
Used instead of tinplate; does not rust easily; used for cans and containers that need to be strong and keep food safe |
|
Stainless Steel |
Returnable containers, large storage and transport containers |
Does not rust because it has chromium; used for big, reusable containers like kegs for drinks; costs more but lasts a long time and does not react with food |
Aluminum foil wraps hot sandwiches to keep them warm. Cans and tins hold drinks, sauces, and some ready-to-eat foods. Stainless steel is used for big containers that can be used again for drinks or lots of food.
Pros and Cons
Metal packaging gives strong protection for food. Aluminum and steel keep out air, light, and water. This helps food stay fresh for longer. Metal is tough and does not break easily when shipped. Many metals, like aluminum, can be recycled and used again.
Metal packaging can help cut down on waste if people recycle it.
Some good things about metal packaging are:
- Very strong and lasts a long time
- Easy to recycle, which saves energy and materials
- Light, so it is easy to move
- Keeps food hot or cold well
- Does not rust easily, especially aluminum
But there are some bad sides too:
- Costs more than plastic or paper
- Heavier than some other choices, so shipping can cost more
- Can rust if the coating comes off
- Cannot be composted, so it must be recycled
- Sometimes, plastic inside cans can let chemicals into food
Metal packaging usually costs between $0.2 and $1.0 for each piece. This is more than plastic or paper but less than glass. The chart below shows how much different packaging types cost:
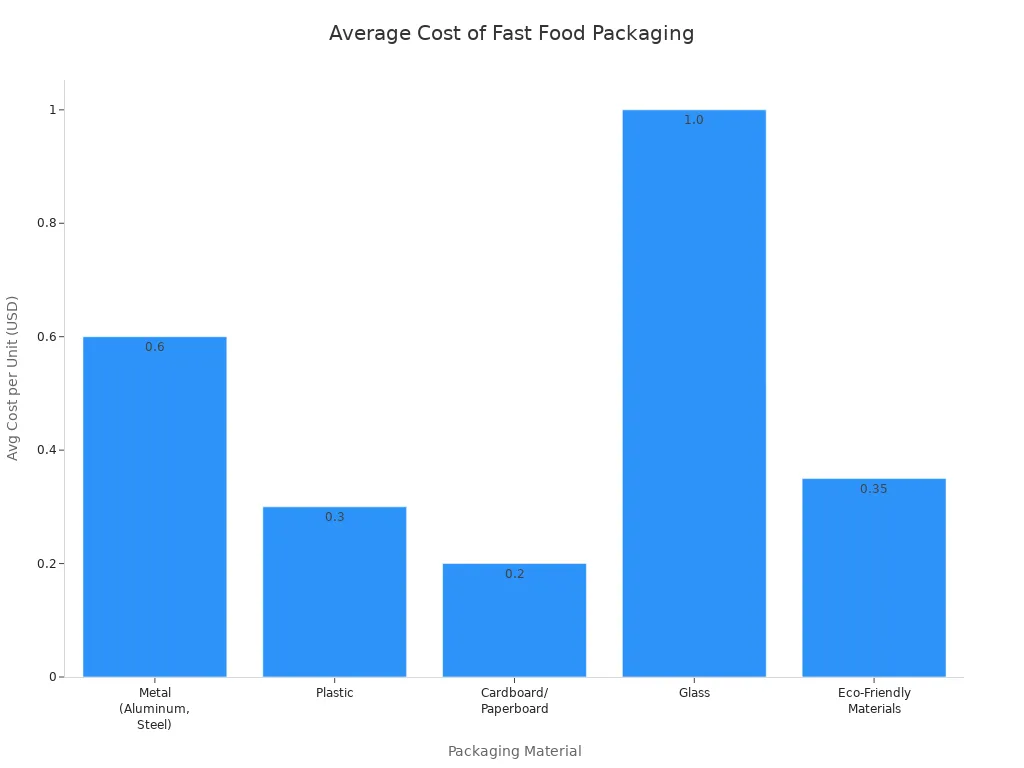
When picking metal packaging, businesses need to think about the good and bad sides. Metal keeps food safe and is good for recycling, but it costs more and must be thrown away the right way.
Glass Packaging
Glass Uses
Glass is not used as much as plastic or paper in fast food. But glass is important for some foods. Fast food places use glass jars for foods that need to stay fresh longer. Some foods in glass are:
- Sauces, dressings, and marinades that add flavor to meals
- Pickles, olives, and relishes that bring crunch and taste to snacks
- Spreads such as jams, jellies, and honey for breakfast or desserts
- Beverages like wine and beer, especially in fast casual or premium settings
Glass keeps air, water, and light away from food. This helps food stay fresh. Glass does not mix with food, so the taste stays the same. Hot liquids can go into glass jars without melting them. This is called hot fill. Glass looks clean and lets people see what is inside. Many people trust glass because of this.
Pros and Cons
Glass packaging has many good points for fast food. It does not react with food, so food tastes right. Glass is safe and keeps food fresh. You can recycle glass over and over. This is good for the earth. Glass is clear, so you can see the food. This helps people trust what they buy.
Glass packaging keeps food safe and fresh, but it also has some problems.
But glass has some bad sides too. Glass is heavier than plastic or metal. This makes shipping cost more and adds pollution. Glass can break if dropped or hit. Broken glass can be dangerous. Making and recycling glass uses a lot of energy. Melting glass takes a lot of heat. This means glass can hurt the earth more than plastic or aluminum, even if it is recycled.
|
Feature |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
|
Safety |
Non-reactive, keeps food safe and fresh |
Fragile, can break and cause safety risks |
|
Environment |
100% recyclable, reusable |
High energy use in production and recycling, heavier weight increases emissions |
|
Practical |
Transparent, supports hot filling, preserves quality |
Heavy, costly to ship, not suitable for all fast food items |
Glass is best for foods that need strong protection and last a long time. Companies must think about the good and bad sides before picking glass.
Composite & Flexible Packaging
Composite Materials
Composite packaging mixes two or more materials together. These packages often have paper, plastic, and aluminum layers. Each layer does something special. Some keep out air or water. Tetra Pak cartons are a good example. They use paper for strength. Plastic seals the package. Aluminum blocks light. This helps food stay fresh for a long time.
|
Packaging Material Type |
Description |
Examples in Fast Food Packaging |
|---|---|---|
|
Paper-based materials |
Give support, can be recycled, are light, and can be changed |
Paperboard, corrugated cardboard (burger boxes, fry containers, drink cups) |
|
Plastic-based materials |
Strong, clear or keeps heat in, used for cups and boxes |
PET (clear beverage cups, condiment containers), Polystyrene foam (hot beverage cups, takeaway containers) |
|
Aluminum-based materials |
Light, keeps heat well, used for wrapping |
Aluminum foil (wrapping burgers or sandwiches) |
Composite materials protect food well and keep it fresh longer. But recycling them is hard. The layers are stuck together. Most recycling centers do not take these packages. This makes more trash and hurts the earth.
Flexible Packaging
Flexible packaging uses thin, bendy materials like plastic films or foil. These can be bags, pouches, or wraps. They are light and easy to carry. Fast food places use them for snacks, sauces, and frozen foods. Common materials are PET, PE-LLD, and BOPA. These films can handle heat, cold, and sharp things.
|
Material |
Description |
Properties |
Examples/Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
|
PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) |
Handles high heat, is a polyester film |
Clear, strong, can be recycled |
Used in composite films, packaging decoration, industrial films |
|
PE-LLD (Linear Low Density Polyethylene) |
White, safe particles |
Strong, tough, handles heat and cold |
Used in flexible packaging films |
|
BOPA (Biaxially Oriented Polyamide, Nylon) |
Tough, clear, and shiny film |
Very strong, hard to poke holes in, keeps out air |
Used in composite packaging for greasy, fried, vacuum-packed foods |
|
Composite Flexible Films |
Many layers of plastic together |
Keeps out water, cold, and sharp things |
OPP/CPP, PET/CPP, Nylon/PE for frozen food packaging and biscuits |
Flexible packaging makes less trash and costs less to ship. But it may not keep food as safe as hard containers.
Pros and Cons
Composite and flexible packaging keep food safe and fresh, but they can hurt the earth.
|
Packaging Type |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
|
Composite Packaging |
Keeps food fresh, lasts long, protects food well, saves money |
Hard to recycle because of many layers, must be burned, costs more to license, people worry about the earth |
|
Flexible Packaging |
Light and easy to use, makes less trash and costs less |
May not protect food as well as hard containers |
New composite materials use plant fibers like flax, hemp, or jute. These cost less and are better for the earth. But most composite packaging is still hard to recycle. Flexible packaging is easy to use, but sometimes does not protect food enough. Both types can harm the earth, so companies try to find better ways.
Takeout Packaging Trends
Eco-Friendly Materials
Many fast food brands now pick eco-friendly materials for takeout. They want to follow new rules and make customers happy. People care about the earth and want packaging that breaks down or can be used again. Companies use things like bagasse, bamboo, and recycled paper. These choices help cut down on trash and pollution.
- KFC uses paperboard that can be recycled and comes from safe forests.
- McDonald’s is trying out reusable cups with TerraCycle’s Loop program.
- Burger King uses packaging made from unbleached paperboard and recycled fiber.
The table below lists common eco-friendly materials for takeout:
|
Material Type |
Examples |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Biodegradable |
Wood, paper, sugarcane bagasse, bioplastics |
Breaks down on its own and helps the soil. |
|
Compostable |
Bagasse, PLA, CPLA, bioplastics |
Turns into natural parts in compost, safe for the earth. |
|
Recycled Content |
Recycled paper, cardboard, plastics |
Made from old things, helps cut down on waste. |
|
Plant-Based |
Bamboo, sugarcane fiber, agave, palm leaves |
Comes from plants, not oil, and grows back fast. |
|
Reusable |
Bioplastics, stainless steel, glass |
Can be used many times, good for cups and cutlery. |
Eco-friendly takeout packaging helps brands show they care about the planet. It also gives people less plastic and more green choices.
Innovations
Takeout packaging has changed a lot in the last few years. Companies use smart designs and new materials to make better takeout packaging. They want food to stay fresh and safe when it is delivered. Many brands use boxes that keep heat in and stop water from getting in. Vented boxes help fried foods stay crispy. Stackable containers make it easy to carry many meals.
- Smart packaging uses QR codes to tell where food comes from and how to recycle the box.
- Some packages have special coatings that fight germs or keep food fresh longer.
- Simple designs use less material but still protect food and show off the brand.
- Edible packaging, like seaweed straws, is starting to show up in some places.
Big brands are leading the way. McDonald’s wants to use only renewable or recycled materials for all packaging by 2025. Burger King is testing reusable cups and lids without straws. These changes help brands earn trust and keep customers coming back.
Takeout packaging is now a big part of eating out. It must be good for the earth, easy to use, and keep food tasting great.
The best takeout packaging uses green materials and new ideas to help both businesses and customers. These trends show that more people want to help the planet and get better service.
Comparing Food Packaging Materials
Quick Reference Table
Picking takeout packaging can be tricky. Every material has good and bad sides. Some keep food warm. Others are better for the earth. The table below compares popular fast food packaging materials. This helps people and businesses choose what works best for them.
|
Material |
Main Pros |
Main Cons |
Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Plastic |
Strong, leak-proof, keeps food fresh |
Hard to recycle, pollutes environment |
Sauces, drinks, wet foods |
|
Paper/Cardboard |
Recyclable, lightweight, easy to print |
Weak with moisture, short-term use |
Burgers, fries, wraps |
|
Metal |
Durable, keeps food hot, recyclable |
Heavy, costly, not compostable |
Hot sandwiches, canned drinks |
|
Glass |
Non-reactive, reusable, clear |
Breaks easily, heavy, high energy to make |
Sauces, drinks, premium foods |
|
Composite |
Long shelf life, protects food well |
Hard to recycle, more waste |
Juice boxes, milk cartons |
|
Flexible |
Lightweight, saves space, cheap |
Less protection, hard to recycle |
Snacks, condiments, frozen foods |
|
Eco-Friendly |
Breaks down, less waste, renewable |
Often costs more, less durable |
Salads, wraps, green takeout |
Tip: Using eco-friendly or recyclable packaging helps cut down on trash and pollution.
Many fast food places use more than one material. They want packaging that keeps food safe and follows new rules. Some brands add special coatings to paper to make it stronger. Others try plant-based plastics for greener packaging. The best choice depends on the food, how long it needs to stay fresh, and how it will be thrown away.
People care about the earth and want easy-to-recycle packaging. Businesses that pick smart packaging can save money and earn trust from customers.
Choosing the Right Packaging
Key Factors
Picking the best takeout packaging depends on many things. Restaurants need to match packaging to the food. Ice cream needs containers that stay cold. Hot meals need boxes that keep heat in. The right material keeps food fresh and safe. It also helps food keep its shape and taste. Packaging should fit the type of food. Some containers can go in the microwave for fancy meals. Boxes with holes help fruits and veggies stay crisp. Cans or special cartons work for foods that are already cooked.
Other important things to think about are:
- How the package looks next to others on the shelf
- If boxes can stack and store easily
- Showing off the brand with colors and logos
- Following the law and being good for the earth
- Balancing cost and quality
- Picking the right size, making it easy to use, and recycling
- Adding stickers with the brand for safety
- Keeping food safe from germs and air
- Making sure it works for delivery orders
Tip: The best takeout packaging helps both the business and the customer.
Food Safety
Food safety is very important for takeout packaging. Different materials like plastics, glass, metals, and paper composites help keep food safe. They block germs and bad chemicals. Good packaging stops harmful things from getting into food. This keeps food fresh and safe to eat. Some materials can let chemicals get into food, especially when hot. Businesses must pick packaging that meets food safety rules. The right packaging keeps food good for longer and helps stop waste.
Sustainability
Sustainability is changing how takeout packaging is made. Many brands now use packaging that is better for the earth. Materials like bioplastics, bamboo, and recycled things use less energy. They make less pollution than regular plastics. These choices break down faster and make less trash. Glass and stainless steel can be used and recycled many times. Bamboo and rice husk grow back and break down in nature. Aluminum boxes are light and easy to recycle. Businesses should not use single-use plastics or containers with BPA. The best packaging can be used again, recycled, or breaks down on its own. This helps stop plastic pollution and lowers harm to the earth.
Fast food packaging materials all have good and bad points. Plastic keeps food safe but can hurt the earth. Paper and cardboard are easy to recycle but do not do well with water. Metal and glass keep food safe but cost more and are heavy. When picking packaging, people think about food type, earth safety, price, and keeping food safe. Both businesses and customers can do these things:
- Ask customers what they think by using surveys.
- Try out new packaging in stores to see how it works.
- Watch how people feel about the packaging.
- Check social media to see what people say.
- Change designs and use more earth-friendly materials.
Learning about new trends and green choices helps everyone pick better packaging.
FAQ
What is the safest material for fast food packaging?
Glass and stainless steel are the safest choices. They do not mix with food or let out chemicals. Many companies use them for sauces and drinks. Paper and cardboard are safe for dry foods too.
Can fast food packaging be recycled?
Most paper, cardboard, glass, and metal can be recycled. Plastic and composite materials are harder to recycle. Food stains or coatings can stop some items from being accepted.
Why do some packages have special coatings?
Special coatings help keep out grease, water, or heat. These coatings keep food fresh and stop leaks. Some coatings make recycling harder, so companies try new eco-friendly ideas.
Are biodegradable packages always better for the environment?
Biodegradable packages break down faster than plastic. They help cut down on waste. Some need special composting places to break down. Not all cities have these, so it depends on where you live.
How can customers help reduce packaging waste?
Customers can use reusable containers and recycle when they can. They can pick brands with eco-friendly packaging. Avoiding single-use plastics also helps. Every small step helps the earth.





